Motion tracking is a technique that allows us to track the movements of objects and use that data for various applications such as entertainment, medicine, military, surveillance, sports, and more.
In animation, VFX, and filmmaking, motion tracking is used to follow the movement of objects in video footage for later processing in post-production to enhance scenes, create new worlds, and add motion graphics and realistic visual effects.
There are many 2D motion tracking tools and post-production software at our disposal, but 3D motion tracking tools are also widely available. Both types aim to identify and track objects on the screen, though they differ in their motion-tracking methods and applications of that motion-tracking data.
In this article, you’ll learn the difference between 2D and 3D motion tracking by diving into each other to understand how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and when to choose between 2D and 3D motion tracking for your project.
If you’re interested in working with 2D and 3D motion tracking software, you’ll find a list of the best tools for 2D and 3D motion tracking.
Are you ready to explore the fascinating yet challenging world of 2D and 3D motion tracking? Let’s get started!
What Is 2D Motion Tracking?
Let's start with 2D motion tracking, typically the first type we learn and which you may be more familiar with. 2D motion tracking is powered by 2D object detection, which identifies and locates objects on your footage but only within a two-dimensional space.
2D motion tracking can track an object’s position, rotation, scale, and skew in two dimensions. It can also track the same parameters for camera motion represented in X and Y coordinates. 2D motion tracking uses tracking points, features, and planes defined on a reference frame. Then, the software algorithms follow these features and points throughout the video.
In 2D tracking, we can find different methods for tracking objects.
-
Single-point: Single-point tracking follows a specific point in the image. It's used when you want to track position to attach an element like text or a logo to an object on the screen.
-
Two-point: Similar to single-point tracking but tracking two points defined by the user. Two-point tracking helps you when tracking position, rotation, and scale.
-
Corner-pin: This technique tracks four points in the video footage and applies the tracking data to the four corners of the insert object. It's common when replacing screens.
-
Planar Tracking: A planar tracker tracks flat surfaces and textures. It can accurately track perspective and parallax and handles occlusions very well. It's a better resource for screen replacements, wall inserts, object removals, and stabilization.
Some popular 2D motion tracking applications are:
-
Video editing
-
Match-moving
-
Motion graphics
-
Adding text
-
Special effects
-
Videogames
-
Remove or replace objects
-
Remove or replace objects
The main advantages of 2D motion tracking are that it’s easy and quick. It’s a less expensive tool when you only need a quick fix and basic animation, and you don’t require data beyond positions, rotation, scale, and skew. Most video editing software features a 2D motion tracking tool, and it can be versatile once you understand how it works and its limitations.
2D animation and tracking are great, but they come with limitations. You can't accurately track the depth and 3D space of the objects. Complex shots with a lot of camera motion and occlusions can be problematic to track, no matter how skilled you are with the motion tracking software.
You'll soon discover that to keep improving in your VFX career, you'll need to learn to use other tools to adapt to different tasks. That's when 3D motion tracking comes to the rescue when 2D tracking is not enough.
What is 3D Motion Tracking?
In the beginning, 2D motion tracking was all there was. However, professionals soon started wanting to create more realistic effects and track objects with accurate depth and perspective changes to add a sense of volume to your videos' motion graphics and effects.
3D motion tracking uses 3D object detection. It analyzes the video footage to identify objects, just as 2D object detection does. However, 3D object detection can determine the accurate position and orientation in a three-dimensional space.
3D motion tracking also tracks the position, rotations, and scale of an object or camera, but it does so in a three-dimensional space in X, Y, and Z coordinates. It means you can track a moving object even as it moves far or closer to the camera, turns around, and can be viewed from multiple angles.
To work with 3D motion tracking, we require more information from our source clip using multiple methods and techniques to track the objects in three dimensions.
-
3D camera tracking: 3D camera tracking or matchmoving recreates the real-world camera movement in a 3D environment inside your specialized software to allow you to add special effects, replace the background, and insert 3D models and CGI elements into your footage that fit into your scenes.
-
Marker-based tracking: This technique involves placing physical markers on objects to record and track them with your real camera. These markers work as point trackers that follow the object more accurately over the sequence.
-
Motion Capture (Mocap): In mocap, 3D data is generated from hardware that captures a subject's movement with sensors as the markers. This data is then used to replace it with a CGI element or 3D model in post-production. It creates realistic animations that interact with the environment.
-
AI tracking: Recent technological advancements have enabled the identification and tracking of objects without markers. AI models are trained to analyze video footage and identify an object's shape and movement. Video editing and 3D software utilize machine learning to enhance 3D motion tracking capabilities.
3D motion tracking is used in multiple fields:
-
3D animation
-
Realistic special effects
-
Worldbuilding
-
3D environments
-
3D modeling
-
Particles
-
CGI elements
-
Replace backgrounds
-
Change camera motion
-
Virtual reality (VR)
-
Augmented reality (AR)
-
Videogames
-
Medical imaging and analysis
-
Topography
-
Autonomous vehicles
Using 3D motion tracking has many advantages. It's more accurate than 2D motion tracking, vividly representing what exists in the real world. The elements added to the screen can achieve a level of realism that feels natural, as if they were recorded with your real-world camera. It can handle more complex shots with rapid motion and perspective changes of objects moving in all directions and more accurately simulating shadows, lighting, and reflections.
As always, there are disadvantages that you must be aware of. First, it is a complex tool to learn and set up before you start tracking. Professional software can be challenging and time-consuming, requiring a powerful computer with more CPU power to handle the processing.
Setting up for 3D motion tracking takes more time because it requires additional data from your footage, which also needs to be higher quality with good lighting conditions for easier tracking. However, the hard work pays off once you render the final video.
What’s the Difference Between 2D vs 3D Matchmoving and Motion Tracking
Let’s focus on the main differences in this 2D vs 3D motion tracking comparison.
-
Tracking Dimensions
The main difference is how both interact and track the dimensions in the footage. As the name suggests, 2D motion tracking revolves around only two dimensions of flat surfaces with no depth.
3D motion tracking focuses on surfaces and objects with depth, perspective, and rapid movements.
-
Tracking Data
2D matchmoving generates data in the X and Y space to easily follow the object’s horizontal and vertical movement and rotation.
3D adds the Z coordinate to focus on depth and perspective, which can create convincing composite images.
-
Equipment
2D matchmoving requires a simpler setup: a computer program or plug-ins, video footage, and knowledge.

3D requires harder to learn software and other hardware, such as markers, cameras, sensors, and mocap gear.
-
Applications
2D tracking shines with basic tracking in footage with little movement to add labels, move texts, remove objects with simple shapes, and add movement to an object or graphic.
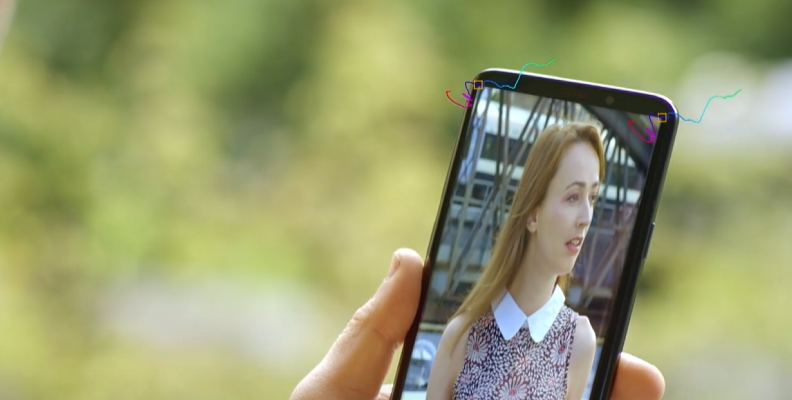

3D tracking can achieve more complex visual effects, background removals, and even seamless inserts of 3D models across all frames.
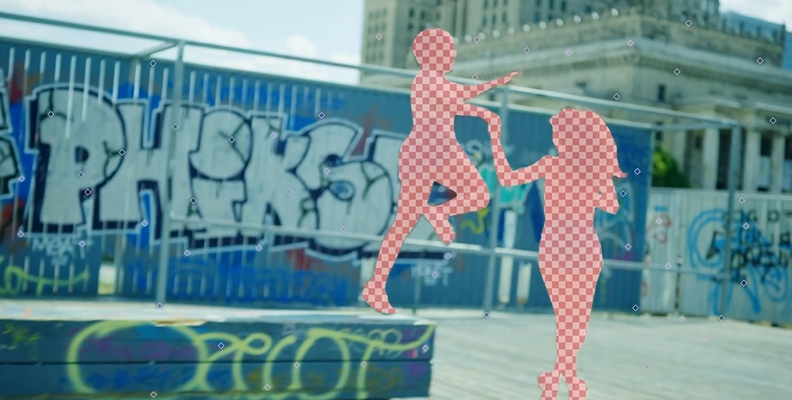

-
Limitations
Regarding complexity and power, 2D motion tracking has difficulty managing rapid motion and camera changes.
However, 3D motion tracking takes longer to achieve an accurate track, and the software demands more computational resources.
How to Choose Between 2D and 3D Motion Tracking?
Now that we know the differences let's decide which one best suits our needs.
-
Type of Motion to Track
Define the type of motions you want or need to track for your project. It will determine which type of motion tracking will achieve the best result.
-
Define Your Goals
Set your expectations. If you don't need to track depth and will work with basic two-dimensional objects, choose 2D motion tracking. But if you need to track depth and achieve a high-quality and professional film with realistic effects, 3D motion tracking and matchmoving is the way to go.
-
Simple vs Complex Effects
If you want to add 3D elements or replace a green screen with a dynamic virtual background, 3D motion tracking is the best choice. For simple tracks from one side of the screen to the other, an overlay, or animated text, 2D motion tracking will perform best.
-
Time Efficiency
2D tracking is faster to perform and requires minimal setup. With 3D motion tracking, the process is more complex, takes more time, and can vary depending on the quality of video footage.
Best Tools for 2D and 3D Motion Tracking
The following list provides an overview of the leading 2D and 3D motion tracking tools. You should research them further to determine which tools suit your workflow and projects.
-
Mocha Pro

Mocha Pro is an award-winning planar tracker for 2D and 3D motion tracking. It has advanced features for rotoscoping, stabilization, and object removal, and PowerMesh can track warped surfaces and organic surfaces such as skin, fabric, and water. The Mocha Pro software is available for Windows and Mac, and the plug-in version can be used inside compatible After Effects, Avid Media Composer, DaVinci Resolve, VEGAS Pro, and more.
-
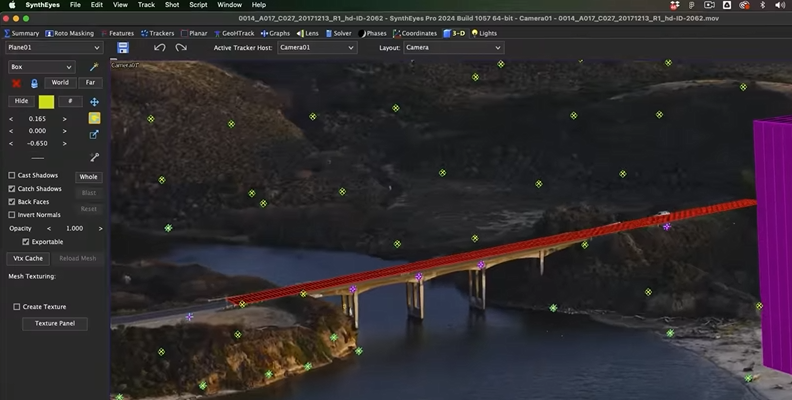
SynthEyes

SynthEyes is a standalone matchmoving software for objects, geometry, planar tracking, and advanced camera solves. It features automation powered by machine learning and advanced 3D motion tracking, streamlining your tracking process with higher results. SynthEyes can export to professional 3D software like Nuke, Flame, Blender, Houdini, and Maya.
-
NukeX

Nuke is professional, industry-standard 2D and 3D motion tracking software and a staple in visual effects. NukeX and Nuke Studio feature a robust 2D tracker, planar tracker, corner pin tracking, and 3D camera tracker, with other machine learning-powered tools to craft custom effects and enhance your 3D workflow. Nuke is supported on Windows, Mac, and Linux computers.
-
Blender

Blender is free, open-source, cross-platform software with 2D and 3D motion tracking features. But don't let the price tag dissuade you. With a built-in 2D tracker, 3D camera tracker, and other 3D modeling and animating features, Blender can be a motion-tracking powerhouse.
-
3DEqualizer
3DEqualizer is an industry-standard matchmoving software used in film and television. It features advanced and precise 2D and 3D motion tracking, stereo tracking, auto tracking, lens distortion, 3D model import/export, and more. 3DEqualizer can handle complex movements with lens distortion.
-
After Effects

Adobe After Effects is a professional motion graphic and VFX tool that is easy to learn. It has a built-in 2D point tracker and a 3D camera tracker for 3D matchmoving. It also features Mocha AE, a streamlined version of Mocha Pro with only the planar tracker available. It's part of the Adobe Creative Cloud subscriptions, which is convenient if you already use other Adobe applications.
Final Words
Motion tracking and matchmoving are vital skills for VFX, filmmaking, and animation. Tracking will always be needed to make quick corrections or create outstanding visual effects. It's important to understand the main differences between 2D and 3D matchmoving and motion tracking. As you learn and face challenges, you'll become more efficient at deciding which motion-tracking option to use.
I'd recommend you try several programs, as they offer different tools that will be part of your skill set. Additionally, consider combining 2D and 3D motion tracking tools to tackle more demanding projects.
Good luck!



